Supply chain management: Definition
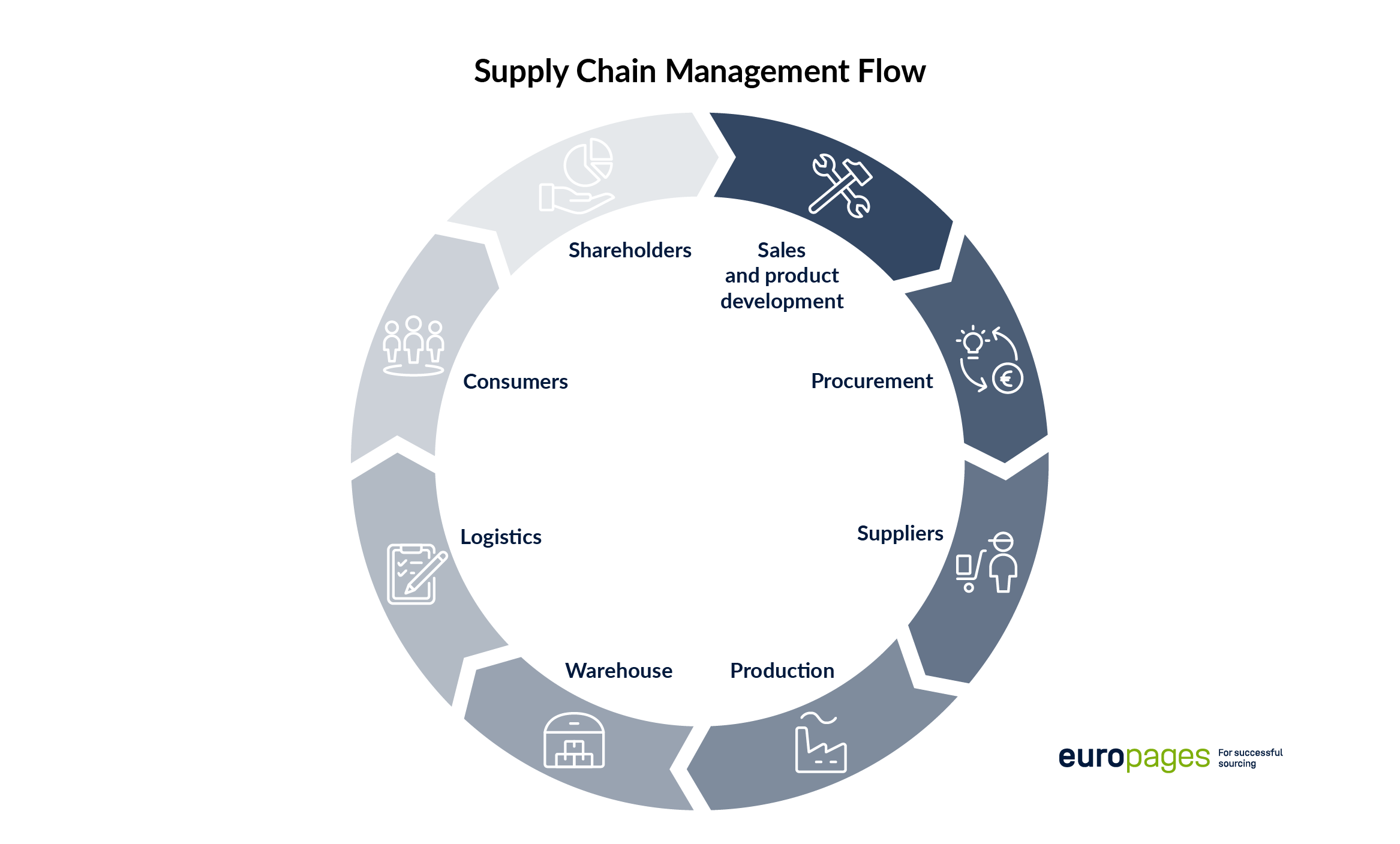
In short, supply chain management (SCM) ensures that a company can deliver its products when and where a customer wants them. It organises everything related to the flow of goods and services and takes into account all processes that convert raw materials into end products and deliver them to the desired destination.
With good management of their supply chain in place, companies can cut excessive costs and transport products quickly and efficiently. Supply chain managers are responsible for managing associated processes in general and avoiding supply bottlenecks. To do this, they need to develop a supply chain strategy, procure raw materials and organise production, distribution and returns, among other things. The best way for them to manage all these activities is with suitable IT systems that integrate all steps and stakeholders in the supply chain centrally.
What is a lean supply chain?
A lean supply chain focuses on producing large quantities at low cost. The focus is on added value for customers. This means trimming processes to make them more efficient and avoiding anything that isn't needed. It involves, for example, just-in-time purchasing and making optimal use of storage capacities.
This type of supply chain focuses more on reliability and predictability than flexibility and adaptability. Production activities will be planned months, if not years in advance, instead of adapting to an ever-changing market. This long-term focus helps find the lowest possible costs for large quantities of goods.
The lean supply chain is suitable under the following circumstances:
- Product type: functional, durable
- Product demand: predictable, consistent
- Product life: long
- Consumer driver: cost-effective
What is an agile supply chain?
The agile supply chain responds rapidly to changes in demand, customer preferences and the sector. It was developed to deal with unpredictability in the market by "delaying". An agile supply chain therefore waits to see what demand is there before manufacturing the end product, thereby responding directly to buying interest, instead of making predictions about this. Some predictions about the market are still necessary however, as parts of a product need to be made early to make the production process fast and efficient.
Agile supply chains are generally used for products with short life cycles or adaptable elements. This necessitates strong partnerships and interactions between stakeholders. It will not be possible to make goods as quickly or efficiently as the agile chain requires unless suppliers collaborate with each other and the market. It tends to entail lower storage costs, because no significant qualities of stock are needed to meet demand.
In these cases, an agile supply chain is the right choice.
- Product type: trendy, fast-moving
- Product demand: market-based, volatile
- Product life: short
- Consumer driver: demand-based
Which concept is better?
In today's fast-paced, global market, many companies opt for the flexibility of an agile supply chain. Its advantages lie in labour and equipment flexibility, risk management, stock placement and integrated planning. It can, however, cause a high level of waste and drive up the prices of certain types of goods. It is therefore not the perfect solution.
In fact, a lot of companies find that they need a hybrid lean/agile solution, to operate as smoothly as possible. This "hybrid supply chain strategy" is able to customise small quantities by making certain parts in advance. This ensures that forecasts and real-time data are equally balanced, which in turn balances out the overall risk level.
Answer the following questions to establish which supply chain strategy is the right strategy for you:
- Which goods do you produce? How consistent are sales of these products throughout the sector?
- Who is your target group? What are their consumer habits?
- How high is the demand for your product today? Will this demand change and fluctuate quickly?
- How quickly does your target market change?
- How will economic fluctuations affect your product, consumers and the spending habits of your sector?
- What does your supply chain look like?
- How do your supply chain partners operate?
Conclusion: There is no solution fit for all companies. You need to consider your product, customers, market and partners in order to develop the right supply chain strategy for your company.

